In the lively hallways of worldwide finance, there is a silent guardian that guarantees the integrity of every transaction, the reliability of all organizations, and the trust of numerous stakeholders. It is the frequently underappreciated Compliance Audit process.
As financial organizations navigate the complicated maze of regulations, the effectiveness of understanding and executing successful compliance audit processes has never been more supreme. But why are these audit procedures so essential? How are they distinct from the internal checks and balances organizations already have? And how is technology – which is recreating every aspect of our lives – being used to improve business compliance audits?
Dive in as we unveil the intricacies of compliance audit procedures, discover their significance for financial organizations, and much more.
Effectiveness of Compliance Audit Process for Financial Enterprises
Every stable financial organization, whether a credit union, bank, or investment company, works under internal controls, codes of conduct, and guidelines. These controls outline how business is conducted and safeguard the organization’s stability and the integrity of its stakeholders. While businesses adopt various standards internally, government bodies also set mandatory standards. These standards are made to safeguard both the organizations and their consumers.
A compliance audit practice, often facilitated by advanced audit management software, is an essential, critical evaluation tool. It evaluates whether a financial company is complying with a set of standards established by its board or government regulators. By undergoing compliance audit processes, financial organizations can assess the effectiveness of their policies, processes, and documentation in alignment with the fundamental regulations in the financial industry.
Why is this procedure so crucial for financial organizations? The answer is evident in the outcomes of noncompliance. Financial enterprises that do not fulfill the set standards generally experience crippling legal consequences, including reputational harm and hefty fines. The stakes are progressively higher in the financial industry, where reliability is the currency.
This is why government regulatory bodies and non-government advisory organizations have been set up to detect areas of noncompliance and provide suggestions to remove them. This support aims to guarantee that financial organizations work within the legal framework and sustain the trust of their stakeholders with the assistance of compliance audit processes.
Difference Between Compliance Audits and Internal Audits
In the technical world of financial supervision, two styles of audits often come to the front: compliance and internal audits. While they share some similarities, primarily in their fact-finding nature, their intentions, methodologies, and associations differ substantially. Understanding these distinctions is essential for financial institutions to guarantee they are self-controlled and compliant with external regulations.
Objective and Focus:
Compliance Audits: A compliance audit, distinct from internal audit management, aims to uncover if a financial institution adheres to external regulatory principles set by government agencies or industry bodies. These compliance audit processes are designed to protect consumers and shareholders and uphold the financial system’s integrity by ensuring institutions operate within the constraints of the law. For instance, a compliance audit evaluates adherence to consumer protection laws or anti-money laundering regulations.
Internal Audits: On the other hand, internal audits are self-examining. They endeavor to assess and upgrade the efficacy of an organization’s risk management, control, and governance processes. While they could touch upon regulatory compliance, their initial focus is on the institution’s internal policies, processes, and operations. For example, the compliance audit processes may review the usefulness of an institution’s internal fraud detection procedures or IT security protocols.
Methodology and Conduct:
Compliance Audits: These are generally conducted by external auditors or regulatory bodies. The methodology involves thoroughly reviewing documentation, processes, and procedures to ensure they align with specific external regulations. Non-compliance can result in penalties, legal actions, and reputational damage.
Internal Audits: These are generally performed by the institution’s internal audit team or external consultants. The approach is more adaptable and modified to the institution’s unique operational structure. It involves assessing the value of internal controls, detecting potential risks, and mentioning improvements, unlike compliance audit processes. The results are primarily for internal use, management decisions, and strategic planning.
The Step-by-Step Mechanism of a Compliance Audit Process
Dealing with financial regulations requires a systematic approach. Unlike internal audit management, the compliance audit procedure is crafted to evaluate an organization’s adherence to laws and regulations. It follows a structured design. Here is the step-by-step process:
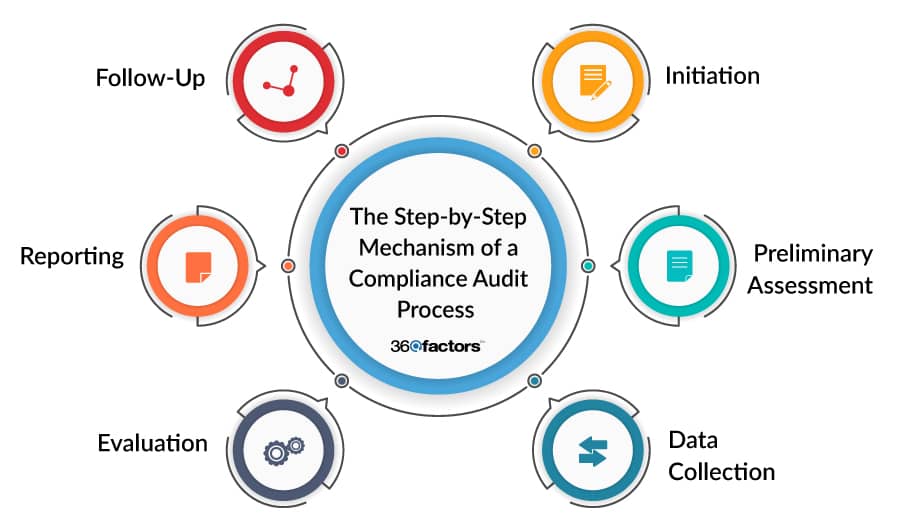
Initiation
The procedure initiates when the financial organization gets connected with an external compliance auditor or is contacted by the regulatory body for an audit. The aim is to assess the organization’s adherence to specific regulatory standards.
Preliminary Assessment
Before going deeper into compliance audit processes, this is the second step in which auditors plan an initial meeting with the company’s representatives. The meeting’s agenda is to set the timeline, define the scope, discuss guidelines, and list the data and documentation needed.
Data Collection
Auditors collect relevant data, including financial records, domestic policies, transaction records, and more. This data builds the foundation upon which audit evaluations are made.
Evaluation
After data collection, auditors evaluate the institution’s operations, policies, and processes against regulatory standards. This involves an accurate review to discover any changes or non-compliance.
Reporting
Post-evaluation, auditors assemble their findings into a thorough report at this phase in most compliance audit processes. This report highlights areas of compliance, points out inconsistencies, and provides suggestions for alignment with regulations.
Follow-Up
After reviewing the report, financial organizations must act on the proposals. Most auditors offer follow-up services, guaranteeing that the recommended corrective methods are executed successfully.
Leverage Technology for Your Business to Lead Compliance Audits
In this technological age, leveraging digitization, especially through tools like internal audit software, is not just an advantage; it’s a need. Financial institutions progressively identify the worth of incorporating advanced technical solutions, such as internal audit software, to modernize and augment compliance audit processes.
Financial organizations must be proactive as the economic environment becomes more complicated and the regulatory world more stringent. Employing advanced solutions like Predict360 Internal Audit and Findings Management Software guarantees compliance and positions financial corporations for success in the face of innovation and efficiency. By integrating such innovative technology, businesses can enhance their compliance audits from broad regulatory exercises into strategic abilities that drive growth and success.
Predict360’s Internal Audit and Findings Management Software is an advanced audit compliance tool designed to reform how financial bodies approach compliance audit processes. Here’s how: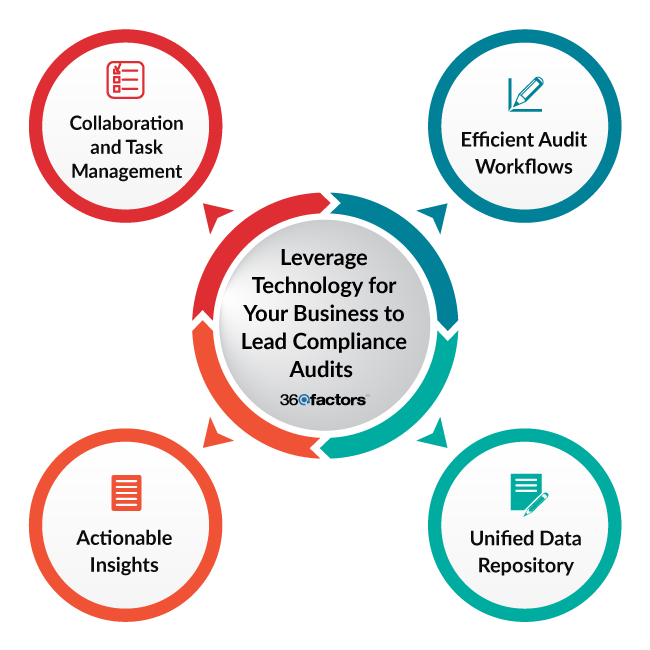
Efficient Audit Workflows:
Predict360 offers a comprehensive workflow that improves audit scheduling, management, and monitoring. It guarantees that businesses extract the highest insights from their evaluations, converting audits from mere regulatory obligations into valuable business decision-making tools.
Unified Data Repository:
The platform makes it easy to secure and store all audit-related information in a single, integrated repository. This unified approach ensures easy access, better data management, and efficient audit execution.
Collaboration and Task Management:
With features enabling collaboration management and audit scheduling for different teams working on compliance audit processes together, Predict360 ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page, improving the efficacy and effectiveness of the audit process.
Actionable Insights:
One of the unique features of Predict360 is its capability to track findings and offer data-driven insights. Relevant business owners are assigned these findings, ensuring that corrective measures are implemented promptly and efficiently.