Home/ Blog / The Agencies’ Guidance for Developing and Implementing Third-Party Risk Management Best Practices in Banks
With the digital advancement of the banking sector, technological innovation has gone to exceptional levels. The sixth wave of innovation based on AI, robotics, and clean tech brings remarkable developments for the financial industry. Financial organizations at the forefront of innovation are digitally transforming for success.
The growing interrelationship of financial organizations with third parties has brought new challenges to risk management efforts. While interdependence gives banks better access to specialized expertise, it also exposes businesses to unforeseen vulnerabilities. Such vulnerabilities include a range of risks, with cyber-attacks being the most prominent. That is why third-party risk management best practices are necessary.
Third-Party Dependence of the Banking Sector
Third-party collaborators have been incorporated to improve operational abilities and bring innovation to the US banking industry. These service providers support advanced loan application processing, improve internal business coordination, and enhance customer experiences.
Some of these vendors can have access to sensitive information, including banking and customer data. Often, they have no robust data safety metrics, bringing vulnerabilities and a lack of business continuity planning in their cyber framework to the financial institution utilizing their services.
Principles Outlined by Regulatory Agencies for Third-Party Risk Management
In the current, versatile banking landscape, third-party risk management best practices have emerged as a necessity. As financial enterprises progressively interconnect their operations with third-party service providers, the possibility for risk multiplies.
Understanding this complex web of partnerships and the challenges it brings, regulatory bodies have stepped forward with comprehensive guidance. It is a collaborative effort from the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC). The guideline underscores the paramount importance of third-party risk management best practices and covers the following areas.
Critical Principles for Third-Party Risk Management
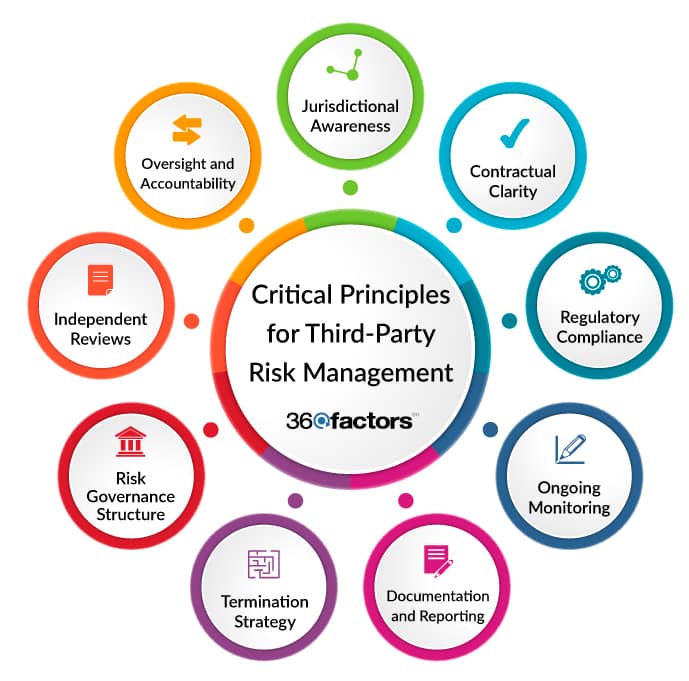
Jurisdictional Awareness
When engaging with international third parties, it’s crucial for banks to understand the legal implications, especially when contracts involve jurisdictions outside the United States. This includes understanding the enforceability of contracts and the potential interpretation by foreign courts.
Contractual Clarity
Contracts should clearly define the terms and conditions, provide remedies for disputes, allow opportunities to cure a breach of contract, and establish clear terms for termination. This can be achieved within an effective third-party risk management framework. Contractual clarity ensures that both parties understand their obligations and the consequences of not meeting them.
Regulatory Compliance
Contracts should stipulate that third-party activities are subject to regulatory examination and oversight. This condition ensures that third-party risk management best practices are implemented and that service providers know their roles and potential liabilities.
Ongoing Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of third-party relationships is essential to confirm the quality of a third party’s controls and their ability to meet contractual obligations. This includes regular reviews, visits, and testing of controls, especially for higher-risk activities. Continuous monitoring covers the following:
- Reviewing reports on the third party’s performance and control effectiveness.
- Conducting periodic visits and meetings with third-party representatives.
- Regularly testing the banking organization’s controls related to third-party relationships.
Documentation and Reporting
Maintaining thorough documentation of all third-party relationships is one of the important third-party risk management best practices, including risk assessments, due diligence results, contracts, and performance reports. Regular reporting to the board or designated committee ensures transparency and accountability.
Termination Strategy
Have a clear strategy for terminating third-party relationships, considering factors like transition of services, costs associated with termination, and managing data retention and destruction risks.
Risk Governance Structure
Whether centralized or dispersed among business lines, a clear risk governance structure ensures that third-party risk management processes are consistent and effective. This includes proper oversight, accountability, and independent reviews.
Independent Reviews
Banks should conduct independent reviews to assess the adequacy of third-party risk management best practices. These reviews should evaluate alignment with business strategy, risk identification, and the effectiveness of controls to build a successful third-party risk management framework.
Oversight and Accountability
The board of directors should provide clear guidance on risk appetite and ensure appropriate policies and procedures are in place. Management should be responsible for implementing these policies and practices.
Importance of Advanced TPRM (Third-Party Risk Management) Technology
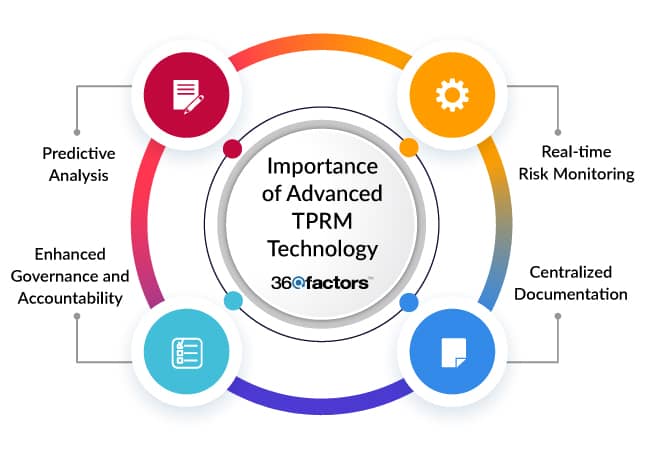
Real-time Risk Monitoring
Advanced TPRM technological platforms offer real-time monitoring capabilities. Instead of periodic checks, banks can now get instant alerts about any discrepancies, potential breaches, or non-compliance issues in third-party operations. This proactive approach aligns with the agencies’ emphasis on continuous oversight and adaptive risk management.
Centralized Documentation
A centralized third-party risk management platform ensures that all documentation related to third-party relationships is stored, organized, and accessible with ease. As the agency guidelines emphasize, this is crucial for transparency, accountability, and independent reviews.
Predictive Analysis
Advanced technology can forecast potential risks by analyzing patterns and trends. This predictive approach allows banks to take preemptive actions, ensuring that third-party risk management best practices are implemented in full and third-party relationships remain compliant and effective in the long run.
Enhanced Governance and Accountability
With the right technology, banks can establish a clear governance framework, ensuring that roles, responsibilities, and oversight mechanisms are clearly defined and implemented.
Predict360 VRM: A Glimpse into the Future of TPRM
The Predict360 Third-Party/Vendor Risk Management (TPRM/VRM) application is a testament to how technology can revolutionize TPRM. This solution offers advanced features that allow financial organizations to track, manage, and report third party risks. Some of its standout features include:
Centralized Data RepositoryIt collects and stores information and documents about third parties in a central data location using configurable checklists, ranging from onboarding to security and periodic supplier performance evaluations.
Automated WorkflowsPredict360 TPRM offers automated workflows that allow employees and external vendor contacts to input information directly into the data system. This can speed up the review and approval of vendor data. This function supports the implementation of third-party risk management best practices.
Risk CategorizationThe platform enables categorization of the type and level of risk for each vendor or third party, ensuring that risks are appropriately managed and monitored.
Advanced Business Intelligence Predict360 third-party risk management software offers embedded Tableau reporting engine, which allows organizations to harness advanced insights, making data-driven decisions more accessible.Challenges Addressed by Predict360 TPRM
Manual TPRM programs often lack dynamic third-party risk management features and the associated regulatory obligations. Disparate software tools like emails, spreadsheets, and shared drives can create barriers to effective third party risk management.
Predict360 TPRM addresses these challenges by:- Offering a more transparent view into third-party performance.
- Streamlining document management to prevent accidental non-compliance.
- Meeting the increasing regulatory requirements for third-party compliance.
- Ensuring that third-party risk management best practices are implemented, and products and services comply with applicable laws, regulations, and standards.
- Making third-party data available for trend analysis.
Conclusion
Third-party risk management (TPRM) solutions are more crucial in the digitalized era than ever. Since regulatory agencies emphasize the importance of robust third-party risk management best practices, implementing these guidelines through advanced TPRM tools offers new opportunities and efficiency for banks and financial institutions.
Request a Demo
Complete the form below and our business team will be in touch to schedule a product demo.
By clicking ‘SUBMIT’ you agree to our Privacy Policy.



